What is a Work Order?
Work orders are an authorization of maintenance, repair or operations work to be completed. Work orders can be manually generated through a work request submitted by a staff member, client, tenant, or automatically generated through a work order management software or Preventive Maintenance (PM) schedule. Work Orders can also be generated via follow ups to Inspections or Audits.
What Does a Work Order Do?
- Offer an explanation of the problem, repair, or installation
- Schedule resources and tools needed for maintenance
- Provide technicians with detailed instructions on the work to be performed
- Document the labor, materials, and resources used to complete the work
- Track all maintenance and repair work that has been performed on each asset
What Is Included in Work Orders?
- Who is requesting the work order
- Who is authorizing the work order
- Who will perform the labor
- What the task is
- When the work order needs to be completed
- Where the work order needs to be performed
- How to complete the task, including necessary parts and other notes
Digitalize to Improve Efficiency
Manually created work orders have long been part of the maintenance world. Though paper-based work orders are easy in some ways, they do not perform as well as a long-term or large-scale solution. Paper work orders can also result in communication delays, extra costs (in both time and money) for data entry, and more. In today’s fast-paced maintenance world, paper-based work orders are inefficient — not to mention environmentally unfriendly.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems such as eMaint CMMS help organizations embrace the power of cloud-based, online software and put an end to repeated phone calls, sticky notes, and missing paperwork. Centralizing and streamlining the work order process improves clarity and gets more work done on time.
How to Use a CMMS for Work Order Management
Work orders are the heart of a maintenance program.The tools within a CMMS help organizations stay up to date on labor, projects, and resources. A CMMS can help organizations take control of both their work backlog and upcoming work, boost productivity, and manage compliance. There are a few keys to effective work order management:
Managing Work Order Requests
Not all work can be planned ahead of time. For corrective work or customer needs, there is a request system. Maintenance managers can tailor workflow processes for request submission, approval, rejection, and completion to the specific needs of their organization. Identifying a workflow process ensures:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are adhered to by all users
- Work goes through an approval process
- Areas of responsibility and expectations are clear for users
- Periodic process auditing is performed
- Valid data is being entered into a CMMS
- Efficient communication flow
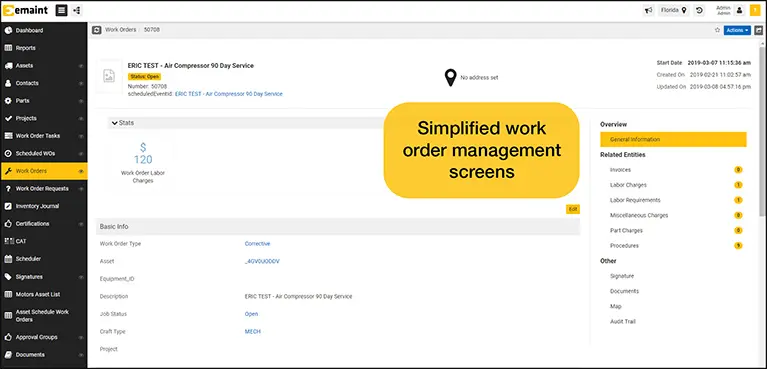
With eMaint, organizations can choose from three work order request submission options:
- Work requestors are given an eMaint user login that allows them to submit requests and view the history and status of their requests
- Work requestors send an email to a designated email address that gets converted into an eMaint work request
- Work requestors submit requests to eMaint through a customized web form embedded on a company’s website or intranet
The work request tools in a CMMS reduce communication errors. Organizations can send requestors automated email alerts when a work request is approved or rejected, followed by an automated email alert with a satisfaction survey once work has been completed.
With modern mobile CMMS solutions, requestors can submit work order requests whenever and wherever using their mobile device. Requestors can attach pictures to their reqs, including pictures of equipment needing repair.
What Is Work Order Software?
CMMS software makes it easy for organizations to increase on-time work completion, improve workflow efficiency, keep track of project due dates, and more.
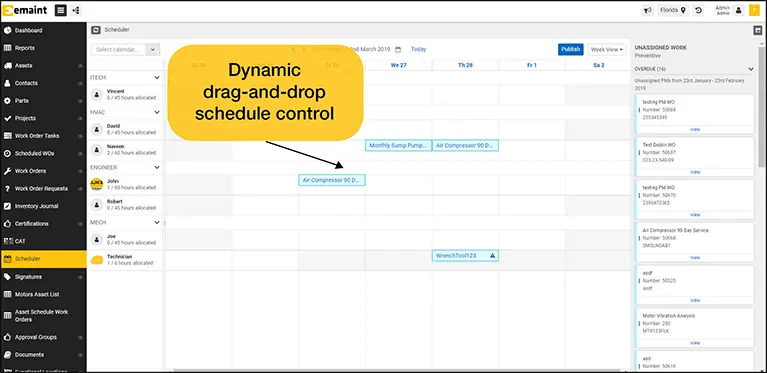
- Work Order Assignment – Using features such as eMaint’s maintenance scheduling tools, maintenance planners and schedulers can directly assign work orders to staff, contractors, or vendors for specific days, times, and locations. Assigned and unassigned work orders can also be viewed on a calendar display, and work can easily be reassigned when necessary.
- Scheduling Calendar – View a calendar by day, week, or month with all labor resources and open work orders, or adjust calendar views and filter work by employee, work order type (such as Preventive Maintenance schedules), and more. Organizations can also use the PM Projection feature to plan upcoming work and ensure the right parts, labor, and tools are available.
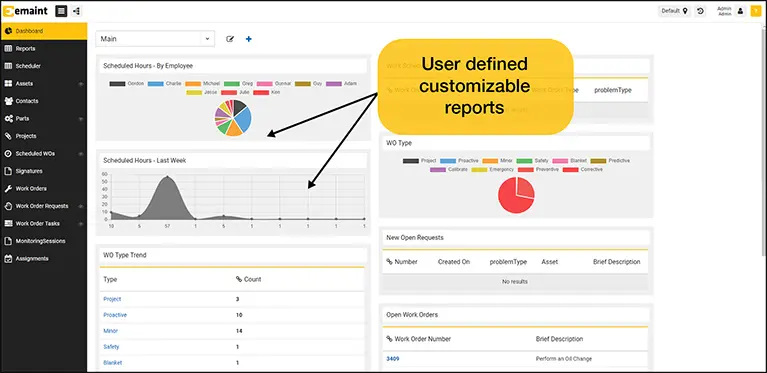
- Reports & Dashboards – Leverage Reports & Dashboards to stay up to date. Categorize work orders by type, technician, department, or any other user-defined field.
- Mobile Maintenance – Using mobile CMMS maintenance services such as eMaint’s MX Mobile, organizations can access real-time data and perform functions throughout their facilities and on the road, including submitting and approving work requests, signing and closing out work orders, and more.
Tracking Projects
Major overhaul and renovation projects can be a headache, but the management process doesn’t need to be. With eMaint’s project management tools, organizations can easily create projects and assign and track work orders from project inception to completion. A CMMS organizes data in one central place. Assets, inventories, and actions that impact operational goals can all be handled from one platform.
With Gantt Charts, users can get a clear visual understanding of work order completion rates compared to a project’s end date.
